Gastroenterology
Gastroenterology is a branch of medicine focused on the digestive system and its disorders. Diseases affecting the gastrointestinal tract, which include the organs from mouth into anus, along the alimentary canal, are the focus of this specialty.
Hepatology or hepatobiliary medicine, encompasses the study of the liver, pancreas and biliary tree is traditionally considered a sub-specialty of gastroenterology.
A group of gastroenterological diseases includes gastritis of different forms (chronic or acute), colitis, peptic ulcer disease, stomach ulcer, unstable colon, colitis ulcerosa, chronic cholecystitis, biliary dyskinesia, pancreatitis.
In case you have any symptoms of these diseases you should see a gastroenterologist.
Symptoms can be different, but all of them start from discomfort and pain in the digestive tract. Pain in the digestive tract is usually the first symptom, usually it is spasmodic stricture or spasm in liver canal. Pain can speak about ulcerous defect in stomach or dodecadactylon.
Usually, people feel gastroenterological pain when the disease is developing and ulceration is spread to other organs, as a result the area of inflammation is growing. Gastroenterological pain can have different character: it can be dragging or dull pain; acute or lancinating.
The next symptoms, appearing in case of gastroenterological diseases, are vomit and nausea. They appear in case sense receptors excitation in esophagus, stomach, bileduct or abdominal membrane.
Dysphagia (difficulty in swallowing) is one of gastroenterological symptoms, appearing when there are pathological changings in alimentary canal and organs.
Icterus (jaundice, a yellowish pigmentation of the skin) is a right symptom of liver disease, signalizing about cirrhosis, hepatitis, mechanical blockage by gallstones or tumor in bile passages.
Diagnostics.
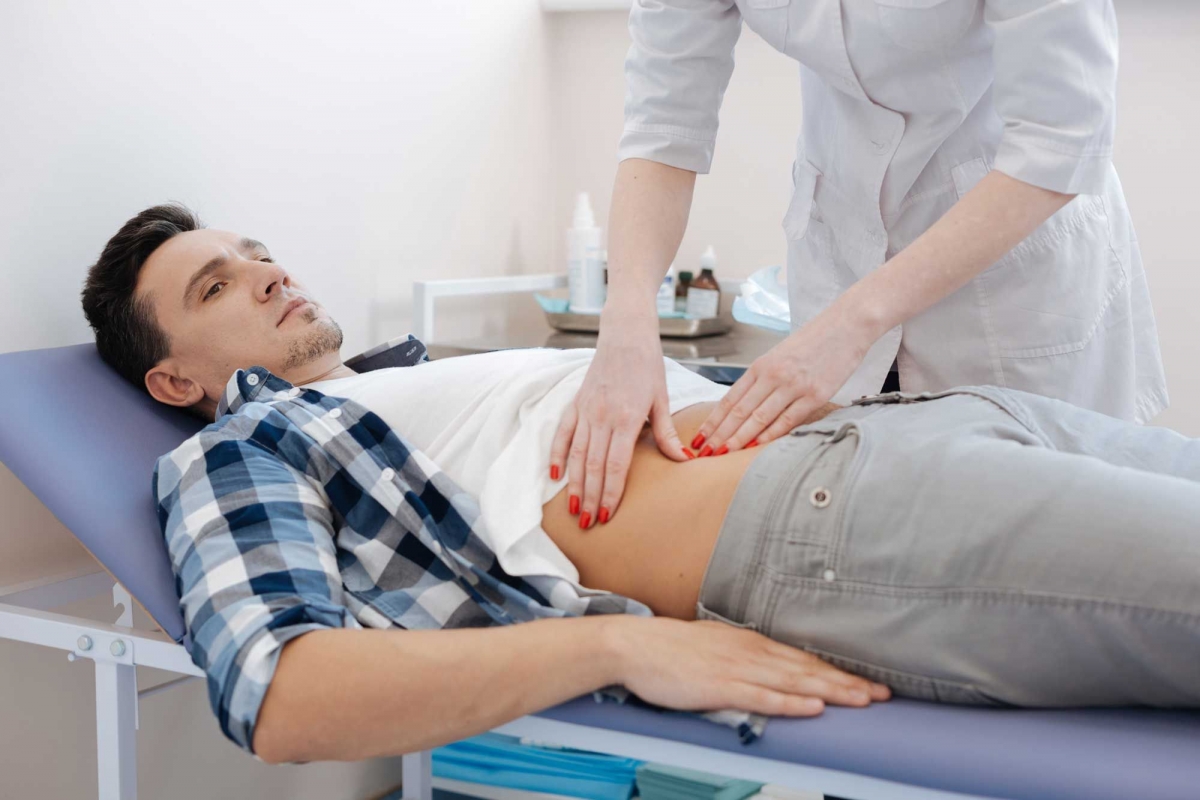
The first universal and objective diagnostic method is belly examination, including simple examination (visual analysis), palpation, tapping and listening. During examination a gastroenterologist pays attention to inflation, hollowness and symmetry of patient’s abdomen. Palpation allows to detect a tumor, see sizes of abdomen organs (liver, gall bladder and others) and fix pain localization. Listening helps to examine enterokinases and detect noises. Tapping can help to catch availability of gas and liquids in peritoneal cavity.
Another diagnostic method is an instrumental one. Fiber optics is always used during diagnostics.
Instrumental methods: colonoscopy of straight intestine and sigmoid colon (for colon diseases), esophagogastroduodenoscopy (in stomach, esophagus, dodecadactylon diseases), proctosigmoidoscope (for diseases of straight intestine and sigmoid colon), endoscopic cholangiopancreatography (for diseases of bile duct and pancreatic duct), celioscopy (examination of abdominal membrane), biopsy (usually liver biopsy).
Contrast-enhanced screening is often used for gastroenterological diagnostics (for diagnostics of diseases in small and large intestine, stomach, dodecadactylon), as well as ultrasound scanning (for diagnostics of pancreatitis, availability of stones and tumors)
Toady gastroenterologists can successfully use functional tests. For all sorts of gastroenterological diseases doctors always order a stool, urinary, blood, bilis tests and stomach analysis.
Gastroenterologists highly recommend people who have problems with gastrointestinal tract do not blame poor food, but make an appointment with specialists as soon as possible. Russian doctors will give a recommendation about food and ration to help your alimentary system and avoid stress.

«Health and Travel» is there for you!


